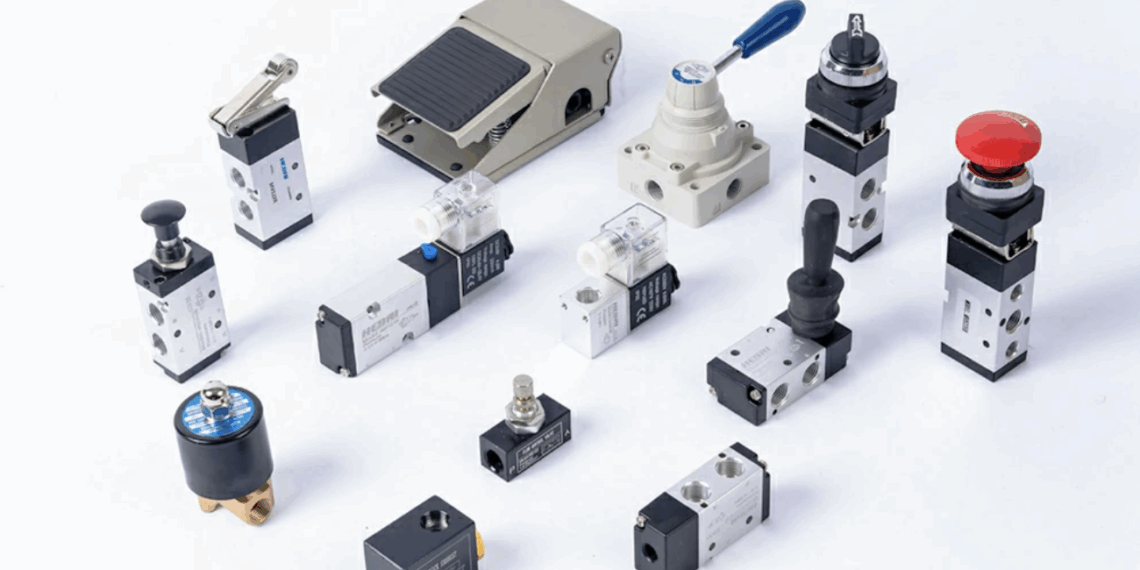
Automation in the present changing world of industry has become the key to efficiency and accuracy in the industry. Conveyor systems and robotics are leading the charge in this change, and the motion control components demanded have to possess a desired nature of accuracy and durability. The pneumatic guided cylinder is just one of the components and has its significant role in automating the tasks which require a repetitive, linear motion under side loads. These cylinders are renowned to be very stable and small in their footprint to be useful in the systems that require high throughput activity without compromising performance. Having an expert automation parts distributor would assure the manufacturers of their abilities to obtain the appropriate pneumatic components to use in their design and performance objectives.
Understanding the Function of Pneumatic Guided Cylinders
A pneumatic guided cylinder refers to a type of linear actuator that has added guidance mechanisms i. e. guide rods or bearings, to ensure it does not spin when operated and ensures that the lateral loads are accounted into the mechanism. This means that it is able to fit in a task that involves repeatable precision like clamping, pushing and lifting. In comparison with the common pneumatic cylinder, guided variants provide increased alignment and stiffness, which is very important in the systems where inconsistencies might arise due to side forces or migration of the tool. The engineers highly regard the cylinders to perform well within a confined space as well as enjoying high levels of precision. They do not require external guides to work and they are easy to install and less footprint on the overall factory floor space.
First is that they can take axial and side loads without compromising. As an example it is the case in electronics assembly when a delicate component being handled can be placed on PCBs with the help of a guided cylinder, which places this delicate component gently and precisely onto PCBs and the chances of misalignment or any form of damage to these components are reduced. Likewise, they can deliver great force in automotive welding stations whilst maintaining the best alignment of workpieces. Such versatility with durability can be used across all types of industries that need a standard. Once incorporated into an automated system, use of guided cylinders allows high levels of repeatability, even after thousands or to even millions of cycles, particularly when the guided cylinder and automation components are provided by a reliable automation parts supplier featuring quality components and customer service support.
Robotics and Conveyor Systems Integration
Precision motion control afforded by pneumatic guided cylinders is very useful with robotics and conveyor systems. In robots, these cylinders are used in robots to help with pick and place, gripper actuation or alignment tasks that require controlled linear movement. The in-built directional system makes loading of payloads without turning and rocking, which increases the safety and quality of products. An example is that a robotic packaging cell might press box flaps shut using guided cylinders, or insert padding material, depending on very precise stroke limits and zero side play.
Guided cylinders are also typical in conveyor lines, diverters, stoppers, and pushers that need to react to sensor signals as fast and precisely as possible. Such applications require size efficiency and long term operation in harsh environmental conditions. The installed capacities enabling the sensors to directly fit on the cylinder body can also give the operator realtime feedback on the position of the cylinder and this is important during high speed sorting or inspection.
Automation part suppliers and a pneumatic guided cylinder can collaborate to guarantee that the chosen part will suit the set speed, force, and distance specifications, but not at the price of the short-term sturdiness. The availability of customized cylinders in mounting styles, cushions, and load-carrying capacities are also useful in enabling the manufacturer to streamline their systems to achieve optimum throughput.
Choosing Long-Term Value Distributor
The selection of the correct pneumatic cylinder is just half of the quintal, as one also has to think about selecting the right automation parts distributor. Quality distributors can add much more to the availability of products: engineering services, availability of technical documentation as well as customisation. If you require corrosion resistant products, low friction sealing products, or getting the length of stroke you need, a good distributor will get you in contact with top manufacturers such as SMC, Festo or Parker. They also ensure that there is stock backing, which translates to zero downtimes and quick deployment of projects.
A supreme distributor performs the value addition at all levels starting with the selection of the product, integration of the system and after sales support. As an example, when upgrading a system, your distributor can prescribe a drop-in match to an obsolete cylinder without wasting time and making expensive redesigns. Other distributors go further as to offer hands-on training, application engineering and even predictive maintenance products that will increase the life of your pneumatic products.
A skilled distributor assists in hurdling the difficulties such as trade replacements, interoperability and integration arrangements. When companies select the right supplier, all the three elements of the supply-chain procurement process: smooth procurement, timely delivery, and optimized system performance are enjoyed. Additionally, sourcing can be consolidated and make traceability possible with centralized procurement which is essential in regulated industries such as food, pharma and aerospace.
Learning Abilities in Smart Automation
Entering the era of Industry 4.0, factories are becoming smarter and moving to data-driven environments, and guided cylinders are being modified to fit here. Most of the newer model cars include sensors that track the position or provide wear data in real-time, allowing predictive maintenance and a higher degree of operational clarity. Such improvements ensure guided cylinders become more applicable to intelligent machinery, including collaborative robots and automatic inspection stations.
More advanced applications Guided cylinders are being integrated into mobile robotic platforms in order to allow gripper on-the-fly gripping or part manipulation in flexible manufacturing lines. Other systems go so far as to combine guided cylinders with machine vision to automatically change motion depending on part orientation, or the indications of quality. The components that are needed in these innovations should have high repeatability and capability to connect to the digital control systems without difficulties.
The application of guided cylinders can continue to grow in new directions as robotic work cells become agiler and the conveyor systems responsive and quicker. This development puts more emphasis on partnering with an automation parts supplier that is technologically sophisticated, a supplier who would provide directional vision in new technology and even a potential provider of state of the art pneumatic products.
Conclusion
Linear guided pneumatic cylinders play a key factor in controlling linear motion when using robots and conveyor based applications. They are used where alignment of high precision, speed and reliability are required due to their property to resist both rotation and side loads.
The efficiency of these cylinders however lies not just in their design but also on where and how they are sourced. With the help of an established automation parts distributor, manufacturers will not only acquire the necessary parts, but also receive the engineering and delivery capabilities, as well as solutions to their specific needs in the latest automation technologies. Having the correct pneumatic guided cylinder and automation parts distributor, your automation systems in the industries can work with precise, dependable and long-term functionality.